
Introduction: Redefining the Driving Experience
The concept of self-driving cars has transitioned from science fiction to a tangible reality, promising to redefine the driving experience as we know it. These autonomous vehicles are equipped with advanced AI systems that enable full autonomy, reducing human error and enhancing traffic management. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the intricacies of self-driving cars, examining their benefits, challenges, and the road to full autonomy.
The Genesis of Self-Driving Technology
The journey towards self-driving cars began with the integration of basic driver-assistance systems in conventional vehicles. From cruise control to lane-keeping assistance, these systems laid the groundwork for more advanced autonomous technologies. Today, self-driving cars are equipped with sophisticated AI algorithms, sensors, and cameras that enable them to navigate complex environments with minimal human intervention.
The Core Components of Self-Driving Cars
Key Features:
- AI-Powered Navigation: Real-time data processing for seamless navigation.
- Safety Enhancements: Automatic braking, lane-keeping, and collision avoidance.
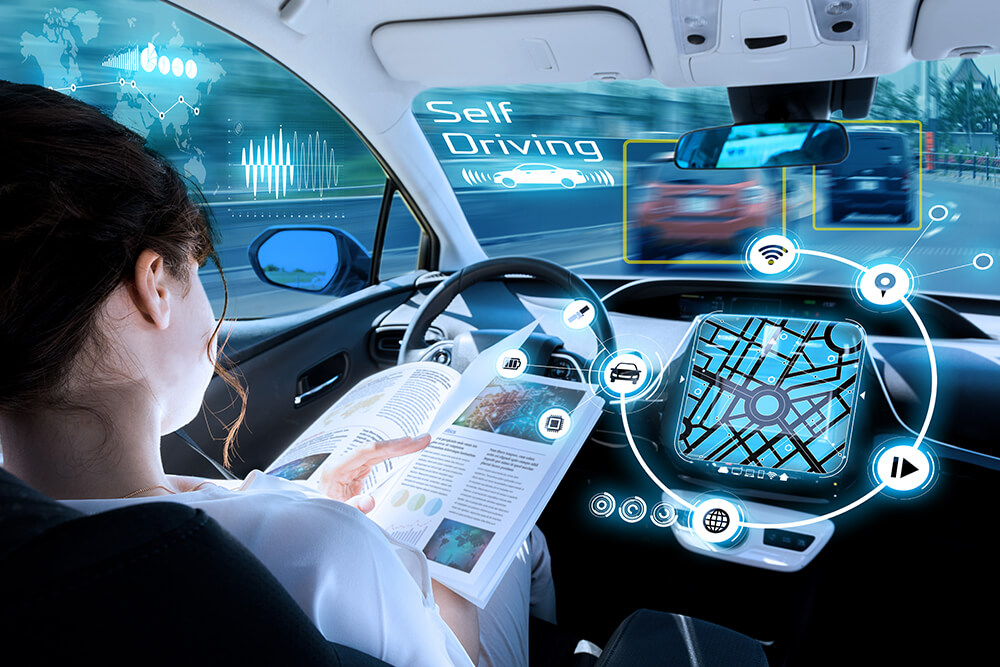
AI-Powered Navigation: At the heart of self-driving technology lies artificial intelligence (AI). Self-driving cars use AI-powered navigation systems that process real-time data from various sensors and cameras. These systems analyze the surroundings, identify obstacles, and make split-second decisions to ensure a smooth and safe journey. The AI algorithms continuously learn and adapt to different driving scenarios, improving their performance over time.
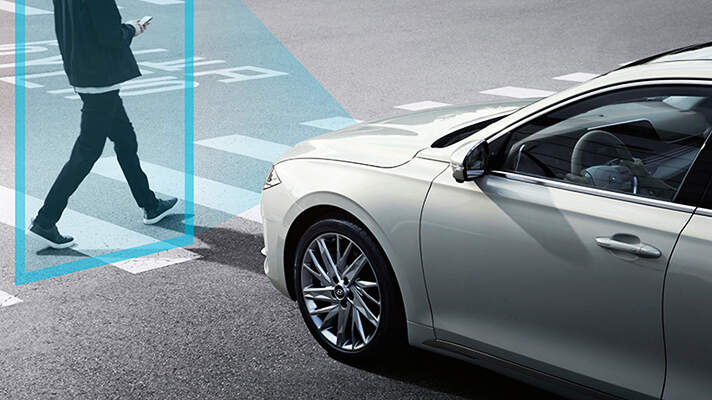
Safety Enhancements: One of the primary motivations behind self-driving cars is to enhance road safety. Human errors, such as distracted driving and fatigue, contribute to a significant number of accidents. Self-driving cars are equipped with safety features like automatic braking, lane-keeping assistance, and collision avoidance systems. These technologies work in tandem to prevent accidents and protect passengers.
The Levels of Autonomy
The journey to full autonomy is divided into five levels, each representing a different degree of automation:
- Level 0: No Automation – The driver controls all aspects of driving.
- Level 1: Driver Assistance – Basic assistance systems like cruise control.
- Level 2: Partial Automation – The car can control both steering and acceleration/deceleration, but the driver must remain engaged.
- Level 3: Conditional Automation – The car can handle most driving tasks, but the driver must be ready to take over when needed.
- Level 4: High Automation – The car can operate independently in most environments, but may require human intervention in certain situations.
- Level 5: Full Automation – The car can handle all driving tasks without any human intervention.
Each level represents a significant milestone in the development of self-driving technology. Currently, most autonomous vehicles on the road are at Level 2 or Level 3, with ongoing research and development aimed at achieving Levels 4 and 5.

The Benefits of Self-Driving Cars
Reducing Traffic Congestion: Traffic congestion is a common issue in urban areas, leading to wasted time and increased pollution. Self-driving cars can communicate with each other and with traffic management systems to optimize traffic flow. By coordinating their movements, they can reduce traffic jams and improve overall efficiency.
Enhancing Road Safety: As mentioned earlier, self-driving cars have the potential to significantly reduce accidents caused by human error. They are equipped with advanced sensors and cameras that provide a 360-degree view of the surroundings, ensuring that potential hazards are detected and avoided.
Improving Mobility: Self-driving cars can provide mobility solutions for individuals who are unable to drive, such as the elderly and people with disabilities. These vehicles offer a level of independence and convenience that was previously unattainable.
Environmental Benefits: Autonomous vehicles can contribute to environmental sustainability by optimizing fuel consumption and reducing emissions. They can adopt efficient driving patterns and reduce unnecessary idling, leading to lower carbon footprints.
The Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the benefits of self-driving cars are compelling, several challenges and ethical considerations must be addressed:
Technological Limitations: Developing fully autonomous vehicles requires overcoming significant technological hurdles. These include improving AI algorithms, enhancing sensor accuracy, and ensuring reliable communication systems.
Regulatory and Legal Framework: The widespread adoption of self-driving cars necessitates a comprehensive regulatory and legal framework. Governments and policymakers must establish guidelines for testing, deployment, and liability in case of accidents.
Ethical Dilemmas: Self-driving cars must make split-second decisions in critical situations, raising ethical dilemmas. For example, how should an autonomous vehicle prioritize the safety of its passengers versus pedestrians? These ethical considerations require careful deliberation and consensus.
Public Acceptance: Gaining public trust and acceptance is crucial for the success of self-driving cars. Many individuals are skeptical about the safety and reliability of autonomous vehicles. Transparent communication and education efforts are essential to address these concerns.
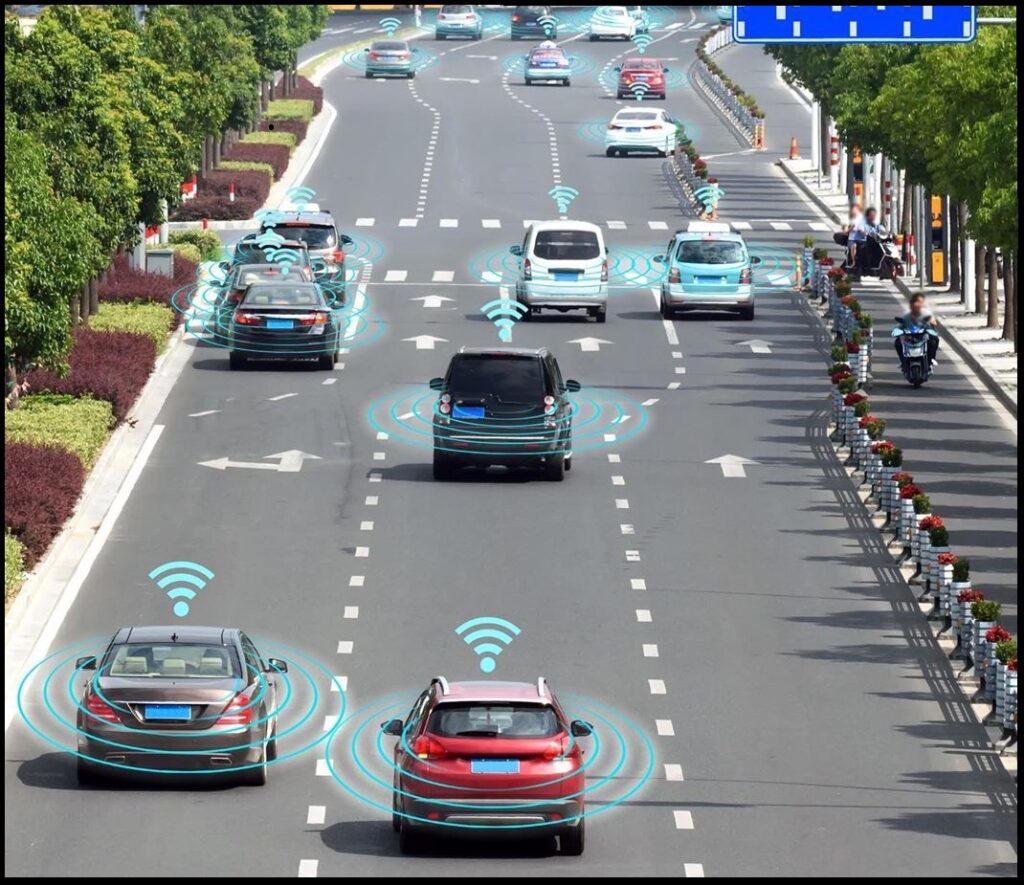

The Road Ahead: Full Autonomy
The path to full autonomy is paved with innovation, collaboration, and continuous improvement. Several companies and research institutions are at the forefront of self-driving technology, conducting rigorous testing and development.
Key Players in the Industry:
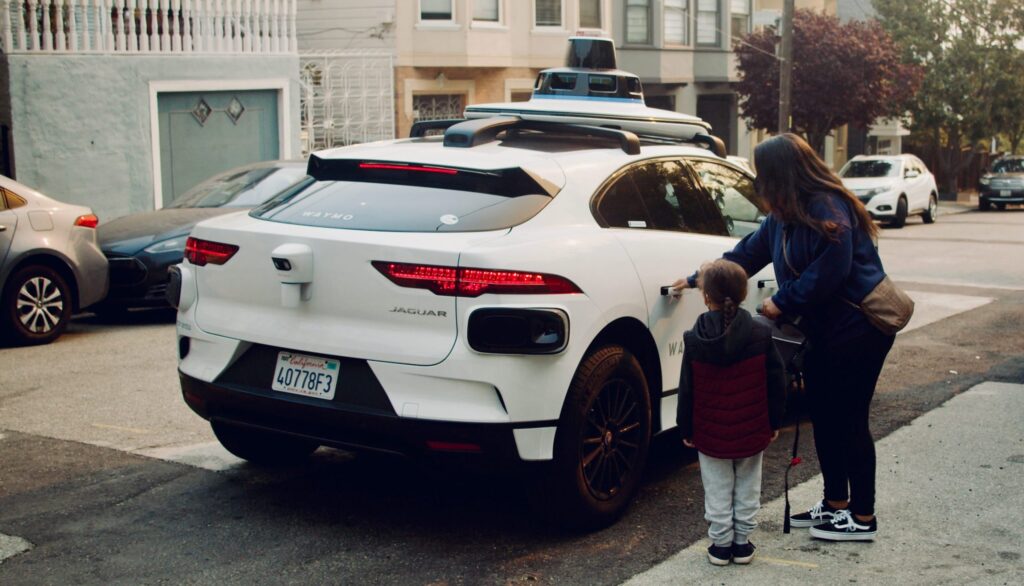
- Waymo: A subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., Waymo is a pioneer in autonomous driving technology. Their self-driving cars have accumulated millions of miles on public roads, demonstrating the viability of Level 4 and Level 5 autonomy.
- Tesla: Tesla’s Autopilot and Full Self-Driving (FSD) systems are designed to provide advanced driver assistance and full autonomy capabilities. The company’s vehicles are equipped with a suite of sensors and AI algorithms for safe and efficient driving.
- Cruise: A subsidiary of General Motors, Cruise is focused on developing fully autonomous vehicles for urban environments. They are actively testing their technology in major cities to refine and validate their systems.
Ongoing Research and Development:
- Sensor Technology: Continuous advancements in sensor technology, including LiDAR, radar, and cameras, are critical for improving the perception and navigation capabilities of self-driving cars.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI algorithms are constantly evolving to enhance decision-making processes and adapt to diverse driving conditions. Machine learning models enable self-driving cars to learn from real-world experiences and improve their performance over time.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Mobility
Self-driving cars represent a transformative shift in the automotive industry, promising a future where driving is safer, more efficient, and accessible to all. As we navigate the road to full autonomy, it is essential to address the challenges, embrace innovation, and foster public trust. The journey may be complex, but the destination holds the promise of a brighter and more connected future.
Engaging Question: What are your thoughts on self-driving cars? How do you envision them changing your daily commute? Share your opinions and experiences in the comments below!





